In a recent blog by Gluware partner NetCraftsmen, it was highlighted that passing security audits does not necessarily mean your IT infrastructure is safe. Read the blog here. Building off the issues and suggestions raised, in this blog we show how having network automation like Gluware in place enables the ability to perform basic compliances checks along with expanding it to the needs of your organization to enhance security.
Compliance Standards
Nearly every IT organization faces significant challenges in keeping up with and implementing IT security compliance. Putting the proper controls in place and performing regular assessments and audits are fundamental to achieving compliance. The challenge often begins with deciphering governmental regulations like FISMA, NIST, DISA STIG, or FEDRAMP. Compliance checks based on 3rd party standards are often the starting point for most organizations since they are well known and frequently used by auditors. IT infrastructure teams (like NetOps and SecOps) will use standards such as those defined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Center for Internet Security Controls (CIS). Is that enough? Having the proper solutions in place can help IT organizations meet that minimum requirement and exceed it with additional security checks.
Using Network Automation for Compliance
Start with Device Configuration Audits
Starting with implementing the automation of compliance audits for device configurations is an excellent way to start. For example, using the Gluware Config Drift and Audit solution, you can run example audits including those defined by NIST, CIS and DISA STIG.
The CIS Benchmarks cover a broad range of technologies. Gluware can be used to execute audits against network devices (like Cisco and Juniper routers and switches).
Using Gluware to audit device configurations, an audit policy is created consisting of required configuration statements and with forbidden statements along with variables or regex to account for changing items like IP addresses, VLAN IDs and others.
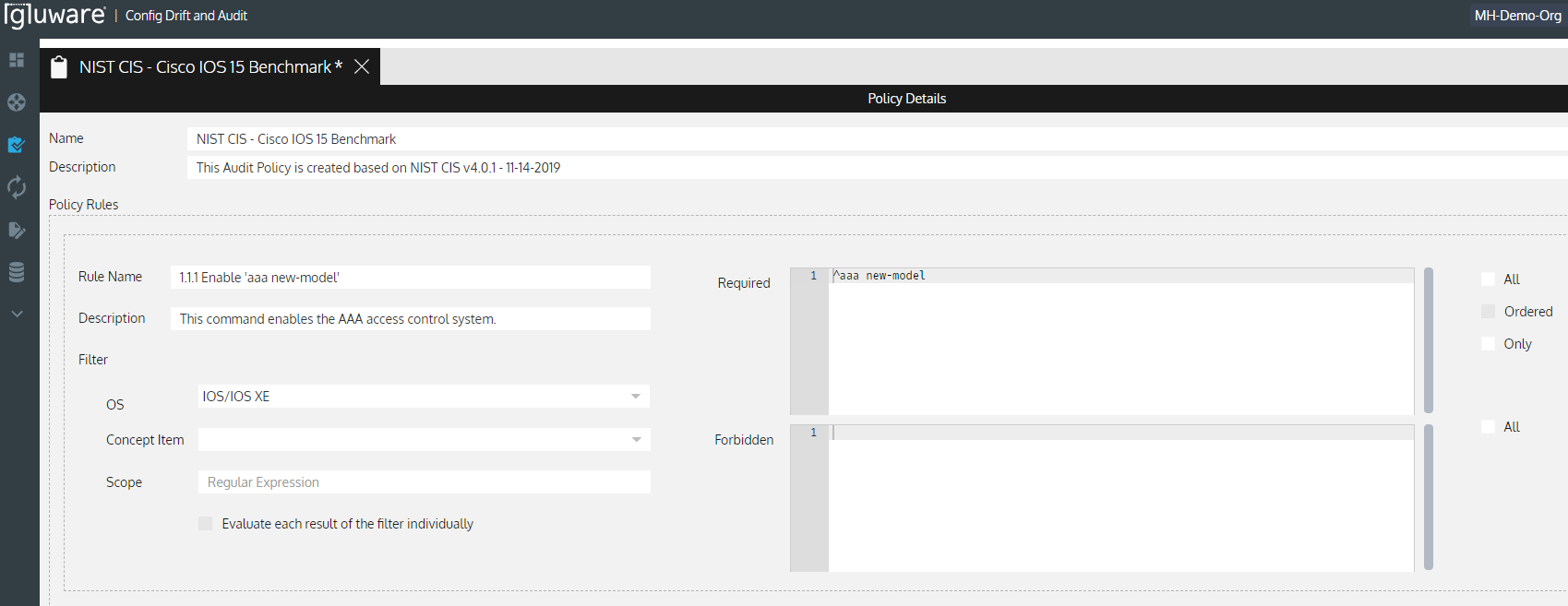 Example audit rule to require AAA authentication
Example audit rule to require AAA authentication
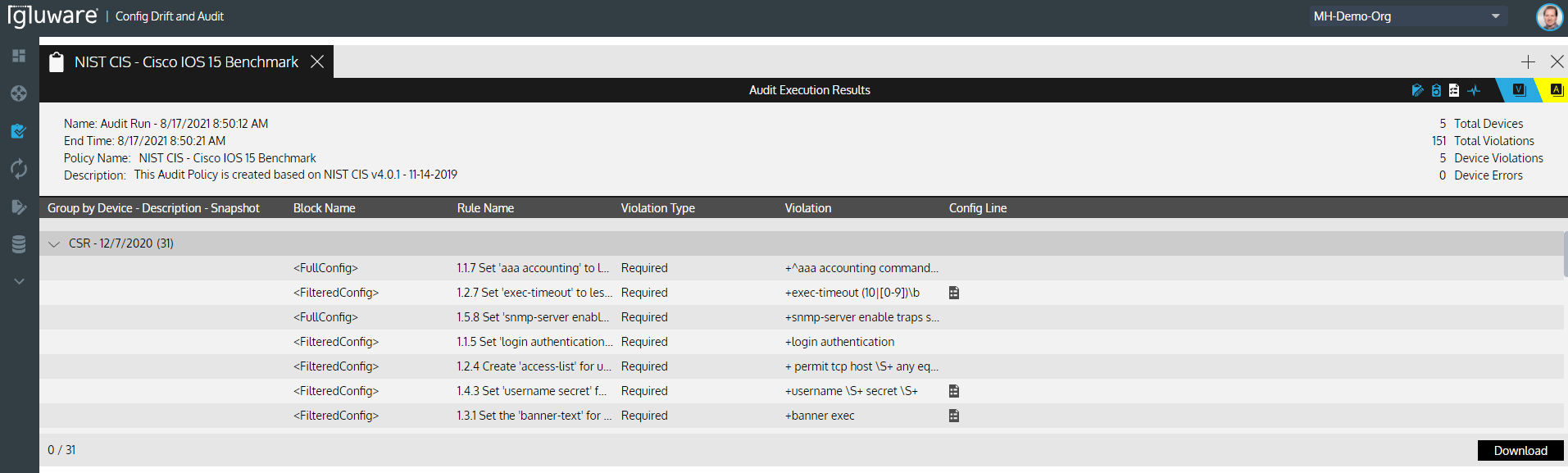 Running the Audit Shows the Summary and Detailed Audit Violations
Running the Audit Shows the Summary and Detailed Audit Violations
Now that you have visibility of the audit violations, you can take the next step to remediate those violations. This can be accomplished using Gluware Config Modeling to define the desired state of each feature and implement the changes reliably and at scale to your network. Once you get your network configuration compliant, you are able to maintain compliance auditing regularly with Config Drift and Audit and implement remediation and ongoing configuration management with Config Modeling.
Automating Essential Network Security Controls
Essential network controls, defined in NIST 800-53 are often difficult to interpret, making them difficult to implement. Isolating these controls enables enterprise IT to have common ground to ensure their network policy meets compliance standards. The specification defines 20 security and privacy control families. The example table below shows how Gluware Intelligent Network Automation can help to deliver essential network controls and how they map to your NIST requirements across many of the control families.
Essential Network Security Controls |
NIST 800-53 Rev. 5 Requirement |
Gluware helps to implement access control by:
|
AC (Access Control) AC-1 Policy and Procedures AC-2 Account Management AC-3 Access Enforcement AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement AC-5 Separation of Duties AC-6 Least Privilege |
Gluware helps to implement audit and accountability by:
|
AU (Audit and Accountability) AU-1 Policy and Procedures AU-2 Event Logging AU-3 Content of Audit Records AU-4 Audit Log Storage Capacity AU-5 Response to Audit Logging Process Failures AU-6 Audit Record Review, Analysis and Reporting |
Gluware helps to implement assessment, authorization and monitoring by:
|
CA (Assessment, Authorization and Monitoring) CA-1 Policy and Procedures CA-2 Control Assessments CA-3 Information Exchange CA-4 Security Certification CA-5 Plan of Action and Milestones CA-6 Authorization |
Gluware helps to implement configuration management by:
|
CM (Configuration Management) CM-1 Policy and Procedures CM-2 Baseline Configuration CM-3 Configuration Change Control CM-4 Impact Analyses CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change CM-6 Configuration Settings |
Network Automation Beyond Compliance
Netcraftsmen raise two additional security-related components to consider:
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
- Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)
ZTA defines an environment where there are no trusted devices, networks, or users. ZTA also defines a Zero Trust Edge (ZTE). ZTA has evolved into a NIST publication, NIST 800-207. Implementing network automation using Gluware, enterprise IT are able to implement and enforce authentication policies on every device in the network using Config Modeling. Gluware can act as the Policy Engine for configuration policies that are applied to the network devices. Gluware can also provide network information and system activity logs that are required. While Gluware does not provide monitoring of traffic flows, it does provide the ability to perform ongoing config audits and monitoring to ensure the network remains in policy using Config Drift and Audit.
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) defines 17 domains in which practices and processes must be implemented. Access Control (AC); Asset Management (AM); Audit and Accountability (AA); Awareness and Training (AT); Configuration Management (CM); Identification and Authentication (IDA); Incident Response (IR); Maintenance (MA); Media Protection (MP); Personnel Security (PS); Physical Protection (PP); Recovery (RE); Risk Management (RM); Security Assessment (SAS); Situational Awareness (SA); System and Communications Protection (SCP); and System and Information Integrity (SII). Similar to NIST 800-53, Gluware can help to automate and implement many of the requirements of this specification related to the network infrastructure.
Automating Network Security as a Process
The NetCraftsmen blog calls out two well-known lifecycle management processes, including:
- Cisco lifecycle process: Prepare, Plan, Design, Implement, Operate, Optimize (PPDIOO)
- IT Information Library (ITIL) process: Strategy, Design, Service Transition, Operations, and Continuous Improvement
Adopting one of these lifecycle processes can enable your organization to stay within a well-defined process and execute lifecycle management. Implementing network automation using Gluware can dramatically accelerate the ability of your organization to meet changing requirements and deliver on the business needs.
To learn more about how Gluware can help enterprise IT implement compliance and improve security through network automation, contact Gluware or request a demo.

